THE MELANOGENESIS
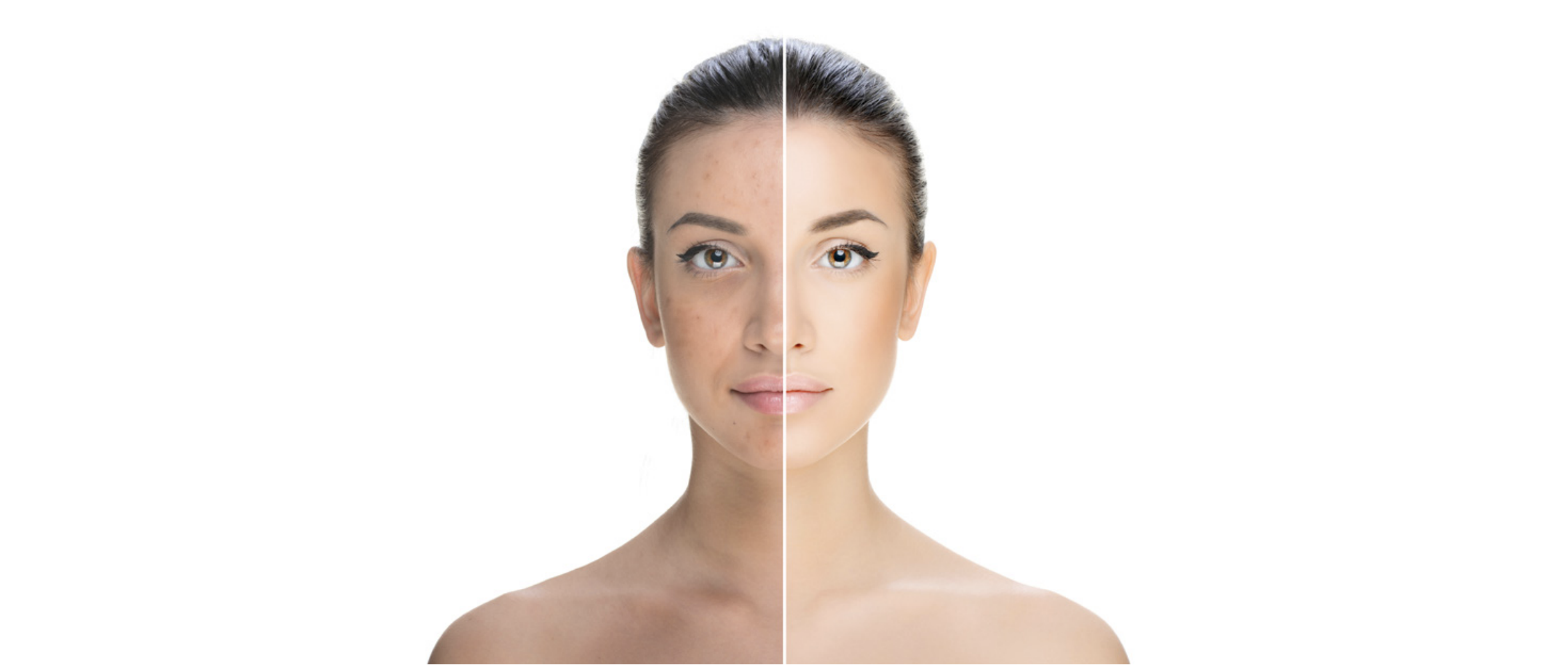
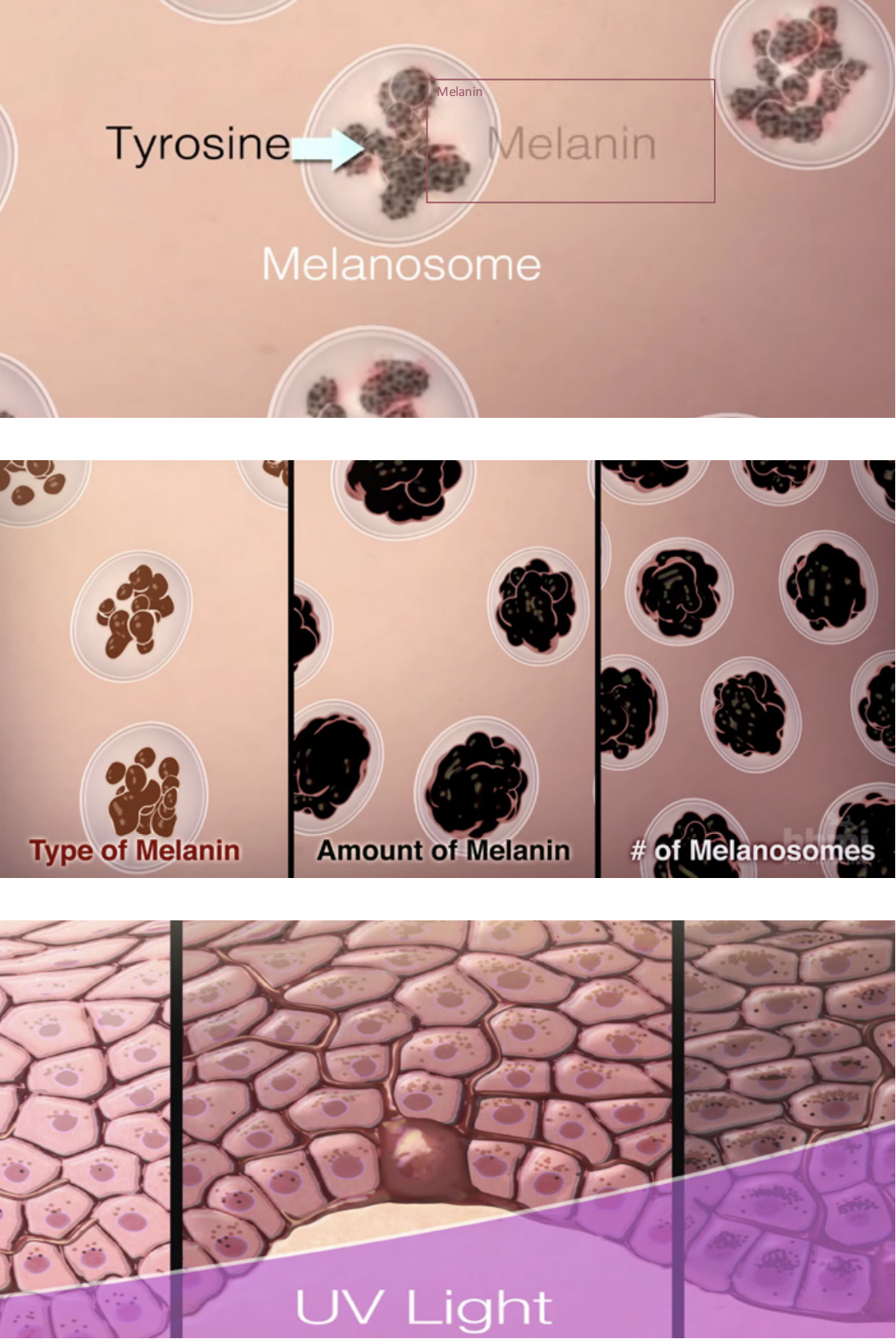
The pigmentation process, called MELANOGENESIS, or the process of Melanin production, begins in specific
basal cells in the epidermis called Melanocytes. The substance Tyrosine
is oxidized then polymerized into
dark Melanin. The Melanin produced
is carried out by granules called Melanosomes to the outermost skin
cells Keratinocytes that constantly shed
off skin and are replaced by new cells.
Differences in skin outer color are due
to the color of the Melanin produced,
the amount of it, and how it ends up
being distributed in the skin (number
of melanosomes). These factors are
hereditary. Other factors can influence
the Melanogenesis such as Hormonal
fluctuation, Skin aging & Sun exposure.
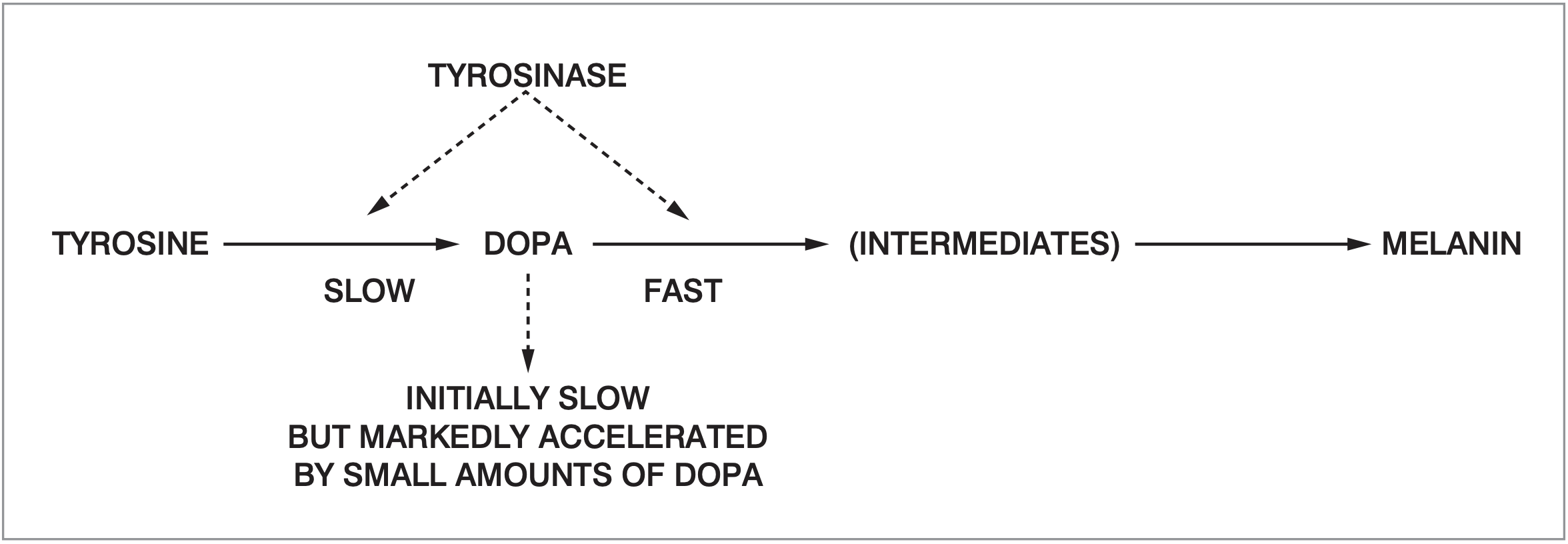
Melanin is produced through a
multistage chemical process known
as melanogenesis, where the oxidation
of the amino acid tyrosine, is followed
by polymerization. There are three
basic types of melanin: eumelanin,
pheomelanin, and neuromelanin.
ABOUT HYDROQUINONE
Cosmetic skin-lightening products containing hydroquinone are often referred
to as “bleaching creams”. Hydroquinone has been banned in KSA, Japan, the
European Union, and Australia. In USA, Any skin-lightening products containing
hydroquinone would only be available with a doctor’s prescription.
- Skin Irritation: Hydroquinone should not be used on skin that is dry, chapped,
sunburned or already irritated, nor should it be applied to an open wound.
- Sun Sensitivity: Hydroquinone makes your skin more sensitive to the sun’s
damaging ultraviolet rays.
- Cancer Causing: Studies in rodents show «some evidence» that hydroquinone
may act as a carcinogen chemical.
- Ochronosis: Hydroquinone also has been linked with the medical condition
known as ochronosis in which the skin becomes dark and thick with Domeshaped yellowish spots and grayish-brown spots even in persons who have used
hydroquinone-containing cosmetics for a short time.
- Some studies also report abnormal function of the Adrenal Glands.